Study Details Advantages of MQL for Micromachining
A recent study found that Minimum Quantity Lubrication increased tool life by 100 times versus dry micromachining of 316L stainless steel.
Share





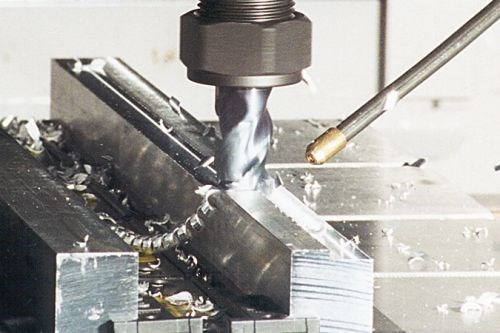
MQL minimizes a shop’s environmental impact by significantly reducing fluid usage and eliminating the need for coolant treatment and disposal.
In a recent e-newsletter, Unist, designer and manufacturer of industrial fluid application systems, cited a study about micromilling 316L stainless steel using Minimum Quantity Lubrication. (MQL is the process of applying minute amounts of lubricant directly to the cutting tool/work piece interface instead of using traditional flood coolants.) The study found that a properly configured MQL process can reduce the built-up edge on a micro cutting tool and increase tool life as much as 100 times compared to dry milling. It cites the importance of quantifying tool runout, wetting both the cutting tool and the workpiece, and properly positioning the MQL stream to maximize lubrication at the chip/material interface.
The report (“Micromilling in Minimum Quantity Lubrication” found in Machining Science and Technology: An International Journal) is available for purchase . Additional information about the advantages of machining with MQL can be found at as well as this blog post and this article about Ford’s use of MQL.
Related Content
-
STLE Opens Registration for 2024 Annual Meeting
The Society of Tribologists and Lubrication Engineers’ 2024 STLE Annual Meeting & Exhibition will take place May 19-23 at the Minneapolis Convention Center in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
-
LNS Chipblaster Provides High-Pressure Coolant Using CNC Interface
The Chipblaster S Series is designed to precisely apply high-pressure coolant where and when required.
-
STLE Hosts Co-Branded Tribology, Lubrication Events
The 2023 STLE Tribology Frontiers Conference and Tribology & Lubrication for E-Mobility Conference will provide attendees with two opportunities to share and learn the latest tribology and lubrication engineering science.

















